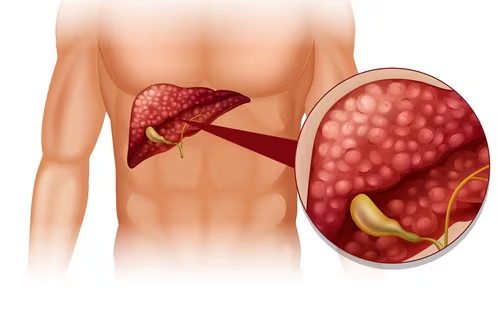
Hardened deposits of bile found in your gallbladder are known as gallbladder stones, also known as gallstones or cholelithiasis. They’re quite common, especially in females. Per the Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the prevalence of gallstones is higher in females vs males (7.6 vs 5.4 percent). Globally, 6 percent of the population has gallstones.
Therefore, learning about gallstones and everyday habits that increase the risk is essential. In an interview with HT Lifestyle, Dr Urman Dhruv, MBBS, MD, director, department of internal medicine, HCG Hospitals, Ahmedabad, highlighted 5 habits that could potentially make you more vulnerable to having gallstones.
Traditional risk factors for gallstone disease
According to Dr Dhruv, approximately 10–20 percent of the national adult population currently carries gallstones. He highlighted: The traditional risk factors for gallstone disease are the four F’s:
- female,
- fat,
- forty,
- and fertile.
“Many studies support the known risk factors for gallstone disease. Overall, obesity, diabetes, metabolic syndrome and abnormal lipid profile predispose to gallstone formation,” he added.
5 everyday habits that increase risk of gallbladder stones
1. Eating a diet high in fat and refined carbohydrates and low in fibre
Your gallbladder’s main job is to store and release bile, which helps your body digest fats. Dr Dhruv pointed out that when your diet is consistently high in unhealthy fats and refined carbohydrates (white bread, pastries, and sugary snacks), it can disrupt the balance of your bile. “A diet low in fibre can also increase your risk. Fibre helps with digestion and bile flow,” he explained.
2. Alcohol
“Excessive alcohol gives you faulty calories and deposition of fat in the liver, and also leads to pancreatic calcification. Alcohol also induces dyslipidemia and inflammation of the stomach. All these factors combine to produce gallstones in a susceptible person,” the expert shared.
3. Rapid weight loss (crash dieting)
While obesity is a known risk factor for gallstones, according to Dr Dhruv, losing weight too quickly can also trigger their formation. “When you lose a lot of weight in a short amount of time, your liver secretes extra cholesterol into the bile,” he explained.

“This can overwhelm the gallbladder’s ability to process it, leading to the formation of stones. It’s recommended to lose weight gradually and at a healthy pace (about 1-2 pounds per week),” he added.
4. Living a sedentary lifestyle
A lack of physical activity is also linked to a higher risk of developing gallstones. Dr Dhruv explained, “Inactivity can contribute to obesity, which is a major risk factor. It also slows down your metabolism and the turnover of bile in your gallbladder. Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and promotes overall digestive health.”
5. Taking unsupervised medicines
Lastly, certain drugs are known to increase the risk of gallstones. Dr Dhruv highlighted, “Newer weight loss modalities like GLP-1 receptor agonists (semaglutide) and dual agonists (tirzepatide) are known to increase this risk.” According to Harvard Health, Ozempic is a semaglutide, and Mounjaro is a tirzepatide medication.
He added, “Estrogen replacement therapies, estrogen oral contraceptives and total parenteral nutrition are also important factors in the causation of gallstones.” He also stressed that one should always remember that ethnicity and genetics have a small role to play, too.